Thyroid Health through Functional Medicine
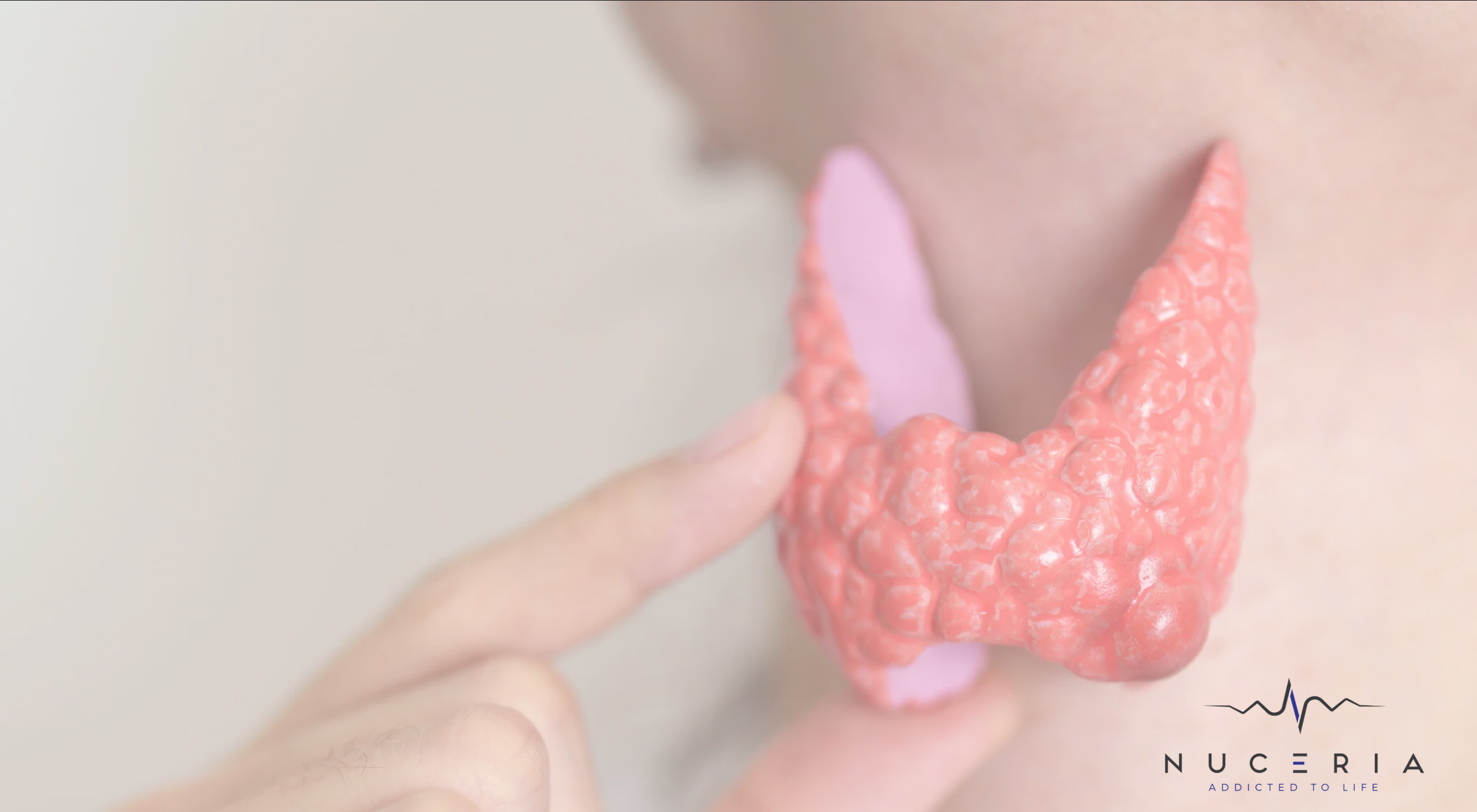
The small yet powerful, butterfly-shaped thyroid gland in the neck is essential for metabolism regulation, maintaining energy levels, and overall well-being. Various thyroid issues can significantly impact the quality of life. Functional medicine aims to thoroughly comprehend and treat these issues by adopting a holistic and tailored approach. This article delves into prevalent thyroid problems and discusses how specific minerals and customized plans can provide relief.
Causes of Thyroid Problems
Thyroid issues arise when the gland produces either too much hormone (hyperthyroidism) or insufficient (hypothyroidism). These imbalances can lead to many bothersome symptoms, such as irritability, fatigue, weight fluctuations, etc. Four prevalent thyroid conditions include Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, goiter (enlarged thyroid), and thyroid nodules. Let's investigate these common disorders, their symptoms, and treatments.
Types of Thyroid Disorders
Hypothyroidism
- Description: When the thyroid gland is underactive, it does not produce enough thyroid hormones.
- Symptoms: Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, depression, and dry skin.
- Common Causes: Hashimoto's thyroiditis, iodine deficiency, and certain medications.
Hyperthyroidism
- Description: An overactive thyroid gland produces excessive thyroid hormones.
- Common Causes: Graves' disease, toxic adenomas, and thyroiditis.
Hyperthyroidism Symptoms
Excessive thyroid hormone production may lead to symptoms that include:
- Restlessness
- Nervousness
- Racing heart rate
- Irritability
- Increased sweating
- Shaking
- Anxiety
- Trouble sleeping
- Thin skin
- Brittle hair and nails
- Muscle weakness
- Weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Frequent bowel movements
- Bulging eyes (in Graves' disease)
Hashimoto's Thyroiditis
- Description: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid gland, leading to hypothyroidism.
- Symptoms: Similar to hypothyroidism, including fatigue, weight gain, and muscle weakness.
- Common Causes: Genetic factors and environmental triggers.
Graves' Disease
- Description: An autoimmune disorder that causes hyperthyroidism by stimulating the thyroid gland to produce too much hormone.
- Symptoms: Bulging eyes, weight loss, rapid heart rate, and irritability.
- Common Causes: Genetic predisposition and environmental factors.
Goiter
- Description: The thyroid gland enlarges, causing swelling in the neck.
- Symptoms: Visible swelling, difficulty swallowing, and breathing problems.
- Common Causes: Iodine deficiency and autoimmune thyroid disease.
Thyroid Nodules
- Description: Abnormal growths or lumps in the thyroid gland can be benign or malignant.
- Symptoms: Often asymptomatic, but large nodules can cause swelling in the neck and difficulty swallowing.
- Common Causes: Radiation exposure and family history.
Functional Medicine Approach
Functional medicine addresses the root cause of thyroid disorders through a personalized and integrative approach. This includes:
Mineral Support
1. Lodine
- Role: Essential for the production of thyroid hormones.
- Sources: Seaweed, fish, dairy products, and iodized salt.
- Consideration: Both deficiency and excess iodine can disrupt thyroid function.
2. Selenium
- Role: Supports the conversion of thyroid hormones and protects the thyroid gland from oxidative stress.
- Sources: Brazil nuts, seafood, and organic meats.
3. Zinc
- Role: Crucial for thyroid hormone synthesis and immune function.
- Sources: Meat, shellfish, legumes, and seeds.
4. Iron
- Role: Necessary for the production of thyroid hormones.
- Sources: Red meat, poultry, fish, and fortified cereals.
Personalized Protocols
Dietary Adjustments
- Focus: Anti-inflammatory diets rich in whole foods, lean proteins, healthy fats, and plenty of vegetables.
- Avoid: Processed foods, gluten (in cases of autoimmune thyroid disorders), and excessive sugar.
Gut Health
- Importance: A healthy gut microbiome supports the immune system and reduces inflammation, which is crucial for managing autoimmune thyroid disorders.
- Approach: Probiotics, prebiotics, and avoiding gut irritants like gluten and dairy.
Stress Management
- Impact: Chronic stress can exacerbate thyroid disorders by disrupting the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
- Techniques: Mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and adequate sleep.
Supplementation
- Tailored Approach: Based on individual needs, supplements like vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids, and adaptogens can support thyroid function and overall health.
Conclusion
Thyroid health is a complex and integral part of overall well-being. Functional medicine offers a comprehensive approach that addresses the root causes of thyroid disorders through personalized protocols and mineral support. By understanding each individual's unique needs, functional medicine practitioners can create effective and sustainable strategies to enhance thyroid health and improve quality of life.
FAQs
1. What distinguishes hypothyroidism from hyperthyroidism?
In hypothyroidism, the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones, leading to fatigue, weight gain, and depression. Conversely, in hyperthyroidism, the thyroid gland becomes overly active and secretes excessive hormones, causing weight loss, nervousness, and a rapid heart rate.
2. Can diet and lifestyle changes help manage thyroid disorders?
Yes, dietary and lifestyle changes can support thyroid health. An anti-inflammatory diet, stress management techniques, and proper supplementation tailored to individual needs can improve thyroid function and overall well-being.
3. What minerals are essential for thyroid health?
Iodine, selenium, zinc, and iron are vital minerals for thyroid health. These minerals support hormone production and conversion and protect the thyroid gland from oxidative stress.
4. How do I get tested for thyroid problems?
To diagnose thyroid disorders, your healthcare provider will likely order blood tests measuring thyroid hormone levels (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH).
5. What are the treatment options for thyroid disorders?
The treatment for thyroid disorders varies with the specific condition. Doctors often treat hypothyroidism with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement, and they may manage hyperthyroidism with medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery. In functional medicine, practitioners address underlying causes by changing diets, managing stress, and adding supplements.
6. Can thyroid disorders be cured?
Doctors can often manage thyroid disorders effectively, although they may not completely cure them. Many people with thyroid disorders live healthy, everyday lives by receiving proper treatment and making lifestyle adjustments. Functional medicine takes a personalized approach to optimize thyroid function and overall health.
Request an appointment here: https://mynuceria.com or call Nuceria Health at (305) 398-4370 for an appointment in our Miami office.
Check out what others are saying about our services on Yelp: Wellness Center in Miami, FL.


 (1).png)

